NAHB expects the 30-year mortgage rate to average 6.17% in
2026 and to reach 6% by 2027.
Long-term mortgage rates have been declining since mid- 2025 and
ended the year at their lowest level since September 2024.
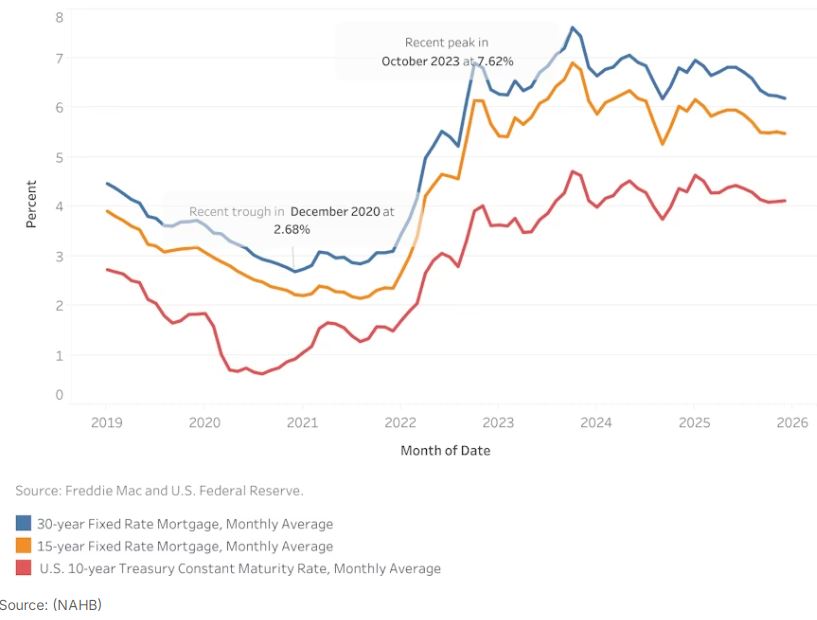
According to Freddie Mac, the 30-year fixed-rate mortgage
averaged 6.19% in December, 5 basis points (bps) lower than
November. Meanwhile, the 15-year rate declined 3 bps to 5.48%.
Compared to a year ago, the 30-year rate is lower by about half
a percentage point, or 53 basis points (bps). The 15-year rate
is also lower by 45 bps.
The 10-year Treasury yield, a key benchmark for long-term
borrowing, averaged 4.12% in December – a modest increase of 2
bps from the previous month. Given forward-looking markets, the
10-year Treasury yield declined during the week preceding the
Federal Reserve’s third rate cut of the year. However, compared
to the prior month, yields ended slightly higher, rising 2 bps,
as labor market data released shortly thereafter pointed to
slowing job gains and rising unemployment rate.
Falling lower mortgage rates have started to translate into
gains as existing home sales edged up slightly in November.
However, this increase remains limited as mortgage rates above
6% are still considered elevated. Nonetheless, as financing
costs continue decline, more households are likely to reenter
the housing market. An NAHB analysis shows that a 25 bps
reduction in the 30-year mortgage rate, from 6.25% to 6.00%,
could bring approximately 1.1 million additional households back
into the buyer pool.
NAHB expects the 30-year mortgage rate to average 6.17% in 2026
and to reach 6% by 2027.
Source:
lbmjournal.com