
Introduction
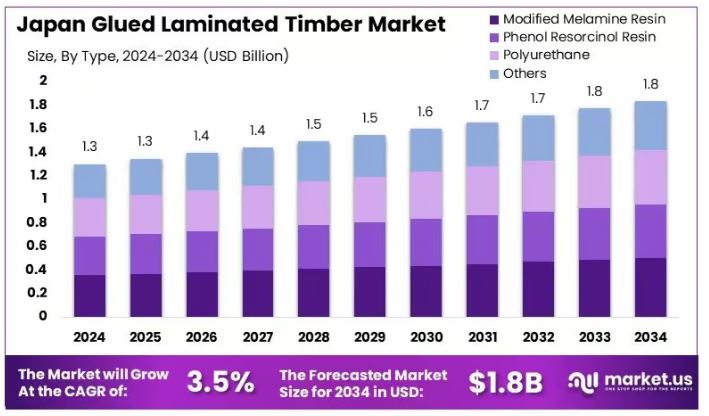
The Japan Glued Laminated Timber Market is projected to reach
approximately USD 1.8 billion by 2034, up from USD 1.3 billion
in 2024, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.5%
during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034.
The Japan Glued Laminated Timber (Glulam) Market is a vital
segment within the country¡¯s engineered wood industry, driven by
the rising demand for sustainable and high-performance
construction materials. Glued Laminated Timber (Glulam) refers
to a structural wood product manufactured by bonding multiple
layers of dimensioned timber with durable adhesives, offering
superior strength, stability, and design flexibility compared to
traditional lumber.
The Japan Glulam market is experiencing steady growth, fueled by
increasing adoption in residential, commercial, and
infrastructure projects due to its environmental advantages,
earthquake-resistant properties, and enhanced load-bearing
capacity. The Japanese government¡¯s commitment to promoting
wooden construction, particularly in public buildings, aligns
with the broader trend of reducing carbon footprints and
enhancing urban sustainability.
Additionally, the demand for Glulam is supported by stringent
building regulations emphasizing earthquake resilience, as
Glulam structures offer high strength-to-weight ratios and
flexibility, making them suitable for seismic-prone areas.
Furthermore, rising urbanization and the shift towards
prefabricated and modular construction methods are augmenting
the demand for engineered wood solutions, including Glulam. Key
growth opportunities exist in the increasing preference for
eco-friendly building materials, government incentives for
timber-based construction, and the expansion of cross-laminated
timber (CLT) applications.
However, challenges such as raw material price fluctuations and
competition from alternative construction materials remain
factors to monitor. Overall, Japan¡¯s Glued Laminated Timber
market is poised for sustained growth, supported by evolving
construction practices, sustainability initiatives, and the need
for resilient building materials in a region prone to natural
disasters.
Key Takeaways
¡¡
-
The Japan Glued Laminated Timber
Market was valued at USD
1.3 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD
1.8 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR
of 3.5%.
-
Modified Melamine Resin led the segment in 2024
with a 27.3%
share, attributed to its durability
and strong adhesive properties.
-
Straight Glulam Beams dominated with 38.2%
share, driven by their preference
for structural applications in construction.
-
Framing
Grade accounted for 34.3% of
the market due to its strength
and suitability for residential buildings.
-
Horizontal Lamination led with 43.2%
share, providing structural
stability and flexibility.
-
Commercial Construction accounted for 34.4%,
supported by the rising
demand for sustainable building materials.
Emerging Trends
Key Takeaways
-
Sustainable Construction Practices: There
is a growing emphasis on environmentally friendly building
materials, leading to increased adoption of glulam due to
its renewable nature and lower carbon footprint compared to
traditional materials.
-
Technological Advancements: Innovations
in manufacturing processes have enhanced the quality and
versatility of glulam products, making them more competitive
with traditional materials.
-
Government Initiatives: Policies
promoting the use of wood in public buildings have
encouraged the adoption of glulam, aligning with
sustainability goals.
-
Urbanization and Infrastructure
Development: Rapid
urbanization has led to a demand for materials that offer
both structural integrity and aesthetic value, positioning
glulam as a favorable option.
-
Seismic Performance: Japan¡¯s
focus on earthquake-resistant construction has highlighted
glulam¡¯s flexibility and strength, making it suitable for
seismic applications.
Top Use Cases
-
Residential Construction: Glulam
is extensively used in housing projects, offering strength
and aesthetic appeal.
-
Commercial Buildings: Its
ability to span large spaces without internal supports makes
it ideal for commercial applications.
-
Public Infrastructure: Glulam
is utilized in public structures such as schools and
community centers, benefiting from its durability and design
flexibility.
-
Bridges: The
material¡¯s strength-to-weight ratio makes it suitable for
bridge construction, providing both functionality and visual
appeal.
-
Renovation Projects: Glulam
is favored in renovations for its adaptability and ease of
integration with existing structures.
Major Challenges
-
Price Sensitivity: Economic
factors have led to increased demand for cost-effective
materials, challenging glulam¡¯s market position.
-
Competition from Alternative
Materials: Traditional
materials like steel and concrete continue to dominate
certain sectors, limiting glulam¡¯s adoption.
-
Supply Chain Constraints: Dependence
on imported raw materials can lead to supply disruptions and
increased costs.
-
Regulatory Hurdles: Building
codes not fully accommodating glulam can impede its broader
application.
-
Market Awareness: Limited
understanding of glulam¡¯s benefits among stakeholders can
slow its adoption in new projects.
Top Opportunities
-
Sustainable Construction Demand: Growing
environmental awareness presents opportunities for glulam as
an eco-friendly material.
-
Technological Integration: Advancements
in manufacturing can lead to innovative glulam applications,
enhancing its market appeal.
-
Urban Development Projects: Urbanization
trends create demand for materials like glulam that offer
both structural integrity and aesthetic value.
-
Government Support: Policies
favoring wood-based construction can boost glulam¡¯s adoption
in public projects.
-
Educational Initiatives: Increasing
awareness and training about glulam¡¯s benefits can expand
its use across various construction sectors.
Conclusion
The Japan Glued Laminated Timber (Glulam) market is set for
steady expansion, driven by rising demand for sustainable
construction materials, government policies promoting
timber-based structures, and technological advancements
enhancing product performance. The market benefits from Glulam¡¯s
structural strength, design flexibility, and
earthquake-resistant properties, making it a preferred choice
for residential, commercial, and infrastructure projects.
Increased urbanization and the adoption of prefabricated
construction further boost its application. However, challenges
such as competition from alternative materials, price
fluctuations, and regulatory constraints persist. Despite these
hurdles, the market remains poised for growth, supported by
sustainability trends, innovative manufacturing processes, and
increasing awareness of engineered wood¡¯s benefits in modern
construction.
Source: news.market.us
|
